
 \n",
"\n",
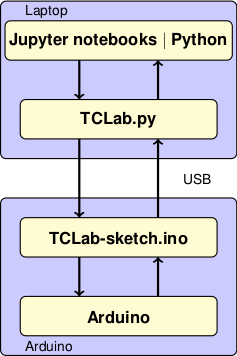
"**_Jupyter notebooks and Python scripts:_**\n",
"The highest level consists of the you code you write to implement control algorithms. This can be done in Jupyter/Python notebooks, directly from Python using a development environment such as Spyder or PyCharm. This repository contains several examples, lessons, and student projects.\n",
"\n",
"**_TCLab:_**\n",
"[TCLab](https://github.com/jckantor/TCLab) consists of a Python library entitled `tclab` that provides high-level access to sensors, heaters, a pseudo-realtime clock. The package includes `TCLab()` class that creates an object to access to the device, an iterator `clock` for synchronizing with a real time clock, `Historian()` class to create objects for data logging, and a `Plotter()` class to visualize data in realtime.\n",
"\n",
"**_TCLab-sketch:_**\n",
"The [TCLab-sketch](https://github.com/jckantor/TCLab-sketch) github repository provides firmware to ensure intrisically safe operation of the Arduino board and shield. The sketch is downloaded to the Arduino using the [Arduino IDE](https://www.arduino.cc/en/Main/Software). Loading firmware to the Arduino is a one-time operation. \n",
"\n",
"**_Arduino:_**\n",
"The hardware platform for the Temperature Control Laboratory. The Python tools and libraries have been tested with the Arduino Uno and Arduino Leonardo boards."
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {
"nbpages": {
"level": 2,
"link": "[1.2.1 Connecting to the Temperature Control Laboratory](https://jckantor.github.io/CBE32338/01.02-The-TCLab-Python-Package.html#1.2.1-Connecting-to-the-Temperature-Control-Laboratory)",
"section": "1.2.1 Connecting to the Temperature Control Laboratory"
},
"slideshow": {
"slide_type": "skip"
}
},
"source": [
"## 1.2.1 Connecting to the Temperature Control Laboratory"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {
"nbpages": {
"level": 3,
"link": "[1.2.1.1 Installation](https://jckantor.github.io/CBE32338/01.02-The-TCLab-Python-Package.html#1.2.1.1-Installation)",
"section": "1.2.1.1 Installation"
},
"slideshow": {
"slide_type": "skip"
}
},
"source": [
"### 1.2.1.1 Installation\n",
"\n",
"The TCLab package is installed from a terminal window (MacOS) or command window (PC) with the command\n",
"\n",
" pip install tclab\n",
"\n",
"Alternatively, the installation can be performed from within a Jupyter/Python notebook with the command\n",
"\n",
" !pip install tclab\n",
"\n",
"There are occasional updates to the library. These can be installed by appending a ` --upgrade` to the above commands and demonstrated in the next cell."
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": 1,
"metadata": {
"nbpages": {
"level": 3,
"link": "[1.2.1.1 Installation](https://jckantor.github.io/CBE32338/01.02-The-TCLab-Python-Package.html#1.2.1.1-Installation)",
"section": "1.2.1.1 Installation"
}
},
"outputs": [
{
"name": "stdout",
"output_type": "stream",
"text": [
"Requirement already up-to-date: tclab in /Users/jeff/opt/anaconda3/lib/python3.7/site-packages (0.4.9)\r\n",
"Requirement already satisfied, skipping upgrade: pyserial in /Users/jeff/opt/anaconda3/lib/python3.7/site-packages (from tclab) (3.4)\r\n"
]
}
],
"source": [
"!pip install tclab --upgrade"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {
"nbpages": {
"level": 3,
"link": "[1.2.1.2 Importing](https://jckantor.github.io/CBE32338/01.02-The-TCLab-Python-Package.html#1.2.1.2-Importing)",
"section": "1.2.1.2 Importing"
},
"slideshow": {
"slide_type": "skip"
}
},
"source": [
"### 1.2.1.2 Importing\n",
" \n",
"Once installed, the `tclab` package can be imported into Python and an instance created with the Python statements\n",
"\n",
" from tclab import TCLab\n",
" lab = TCLab()\n",
"\n",
"TCLab() attempts to find a device connected to a serial port and return a connection. An error is generated if no device is found. The connection should be closed when no longer in use.\n",
"\n",
"The following cell demonstrates this process, and uses the tclab `LED()` function to flash the LED on the Temperature Control Lab for a period of 10 seconds at a 100% brightness level. "
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": 4,
"metadata": {
"nbpages": {
"level": 3,
"link": "[1.2.1.2 Importing](https://jckantor.github.io/CBE32338/01.02-The-TCLab-Python-Package.html#1.2.1.2-Importing)",
"section": "1.2.1.2 Importing"
}
},
"outputs": [
{
"name": "stdout",
"output_type": "stream",
"text": [
"TCLab version 0.4.9\n",
"Arduino Leonardo connected on port /dev/cu.usbmodem142101 at 115200 baud.\n",
"TCLab Firmware 1.4.3 Arduino Leonardo/Micro.\n",
"TCLab disconnected successfully.\n"
]
}
],
"source": [
"from tclab import TCLab\n",
"\n",
"lab = TCLab()\n",
"lab.LED(100)\n",
"lab.close()"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {
"nbpages": {
"level": 3,
"link": "[1.2.1.3 Using TCLab with Python's `with` statement](https://jckantor.github.io/CBE32338/01.02-The-TCLab-Python-Package.html#1.2.1.3-Using-TCLab-with-Python's-`with`-statement)",
"section": "1.2.1.3 Using TCLab with Python's `with` statement"
}
},
"source": [
"### 1.2.1.3 Using TCLab with Python's `with` statement\n",
"\n",
"The Python `with` statement provides a convenient means of setting up and closing a connection to the Temperature Control Laboratory. In particular, the with statement establishes a context where a tclab instance is created, assigned to a variable, and automatically closed upon completion. The `with` statement is the preferred way to connect the Temperature Control Laboratory for most uses."
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": 5,
"metadata": {
"nbpages": {
"level": 3,
"link": "[1.2.1.3 Using TCLab with Python's `with` statement](https://jckantor.github.io/CBE32338/01.02-The-TCLab-Python-Package.html#1.2.1.3-Using-TCLab-with-Python's-`with`-statement)",
"section": "1.2.1.3 Using TCLab with Python's `with` statement"
},
"slideshow": {
"slide_type": "skip"
}
},
"outputs": [
{
"name": "stdout",
"output_type": "stream",
"text": [
"TCLab version 0.4.9\n",
"Arduino Leonardo connected on port /dev/cu.usbmodem142101 at 115200 baud.\n",
"TCLab Firmware 1.4.3 Arduino Leonardo/Micro.\n",
"TCLab disconnected successfully.\n"
]
}
],
"source": [
"from tclab import TCLab\n",
"\n",
"with TCLab() as lab:\n",
" lab.LED(100)"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {
"nbpages": {
"level": 2,
"link": "[1.2.2 Reading Temperatures](https://jckantor.github.io/CBE32338/01.02-The-TCLab-Python-Package.html#1.2.2-Reading-Temperatures)",
"section": "1.2.2 Reading Temperatures"
}
},
"source": [
"## 1.2.2 Reading Temperatures\n",
"\n",
"Once a tclab instance is created and connected to a device, the temperature sensors on the temperature control lab can be acccessed with the attributes `.T1` and `.T2`. For example, given an instance `lab`, the temperatures are accessed as\n",
"\n",
" T1 = lab.T1\n",
" T2 = lab.T2\n",
"\n",
"`lab.T1` and `lab.T2` are read-only properties. Any attempt to set them to a value will return a Python error."
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": 6,
"metadata": {
"nbpages": {
"level": 2,
"link": "[1.2.2 Reading Temperatures](https://jckantor.github.io/CBE32338/01.02-The-TCLab-Python-Package.html#1.2.2-Reading-Temperatures)",
"section": "1.2.2 Reading Temperatures"
}
},
"outputs": [
{
"name": "stdout",
"output_type": "stream",
"text": [
"TCLab version 0.4.9\n",
"Arduino Leonardo connected on port /dev/cu.usbmodem142101 at 115200 baud.\n",
"TCLab Firmware 1.4.3 Arduino Leonardo/Micro.\n",
"Temperature 1: 23.48 C\n",
"Temperature 2: 23.81 C\n",
"TCLab disconnected successfully.\n"
]
}
],
"source": [
"from tclab import TCLab\n",
"\n",
"with TCLab() as a:\n",
" print(\"Temperature 1: {0:0.2f} C\".format(a.T1))\n",
" print(\"Temperature 2: {0:0.2f} C\".format(a.T2))"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {
"nbpages": {
"level": 2,
"link": "[1.2.3 Setting Heaters](https://jckantor.github.io/CBE32338/01.02-The-TCLab-Python-Package.html#1.2.3-Setting-Heaters)",
"section": "1.2.3 Setting Heaters"
},
"slideshow": {
"slide_type": "skip"
}
},
"source": [
"## 1.2.3 Setting Heaters\n",
"\n",
"For legacy reasons, there are two ways to set the power levels of the heaters. \n",
"\n",
"The first way is to the functions`.Q1()` and `.Q2()` of a `TCLab` instance. For example, both heaters can be set to 100% power with the functions\n",
"\n",
" lab = TCLab()\n",
" lab.Q1(100)\n",
" lab.Q2(100)\n",
"\n",
"The device firmware limits the heaters to a range of 0 to 100%. The current value of attributes may be accessed via\n",
"\n",
" Q1 = lab.Q1()\n",
" Q2 = lab.Q2()\n",
" \n",
"Important notes:\n",
"1. The led on the temperature control laboratory will turns from dim to bright when either heater is on.\n",
"2. Closing the TCLab instance turns the heaters off.\n",
"3. The power level of the two heaters may be different. Current versions of the firmware limit maximum power of first heater to 4 watts, and maxium power of the second heater to 2 watts.\n",
"4. In addition to the constraints imposed by the firmware, the power supply may not be capable of providing all of the power needed to operate both heaters at 100%\n",
"5. The values retrieved from these functions may be different than the values set due to the power limits enforced by the device firmware."
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": 18,
"metadata": {
"nbpages": {
"level": 2,
"link": "[1.2.3 Setting Heaters](https://jckantor.github.io/CBE32338/01.02-The-TCLab-Python-Package.html#1.2.3-Setting-Heaters)",
"section": "1.2.3 Setting Heaters"
},
"slideshow": {
"slide_type": "skip"
}
},
"outputs": [
{
"name": "stdout",
"output_type": "stream",
"text": [
"TCLab version 0.4.8\n",
"Arduino Leonardo connected on port /dev/cu.usbmodem14101 at 115200 baud.\n",
"TCLab Firmware 1.4.3 Arduino Leonardo/Micro.\n",
"\n",
"Starting Temperature 1: 23.81 C\n",
"Starting Temperature 2: 23.16 C\n",
"\n",
"Set Heater 1: 100.0 %\n",
"Set Heater 2: 100.0 %\n",
"\n",
"Heat for 30 seconds\n",
"\n",
"Turn Heaters Off\n",
"\n",
"Set Heater 1: 0.0 %\n",
"Set Heater 2: 0.0 %\n",
"\n",
"Final Temperature 1: 28.00 C\n",
"Final Temperature 2: 24.77 C\n",
"TCLab disconnected successfully.\n"
]
}
],
"source": [
"from tclab import TCLab\n",
"import time\n",
"\n",
"with TCLab() as a:\n",
" print(\"\\nStarting Temperature 1: {0:0.2f} C\".format(a.T1),flush=True)\n",
" print(\"Starting Temperature 2: {0:0.2f} C\".format(a.T2),flush=True)\n",
"\n",
" a.Q1(100)\n",
" a.Q2(100)\n",
" print(\"\\nSet Heater 1:\", a.Q1(), \"%\",flush=True)\n",
" print(\"Set Heater 2:\", a.Q2(), \"%\",flush=True)\n",
" \n",
" t_heat = 30\n",
" print(\"\\nHeat for\", t_heat, \"seconds\")\n",
" time.sleep(t_heat)\n",
"\n",
" print(\"\\nTurn Heaters Off\")\n",
" a.Q1(0)\n",
" a.Q2(0)\n",
" print(\"\\nSet Heater 1:\", a.Q1(), \"%\",flush=True)\n",
" print(\"Set Heater 2:\", a.Q2(), \"%\",flush=True)\n",
" \n",
" print(\"\\nFinal Temperature 1: {0:0.2f} C\".format(a.T1))\n",
" print(\"Final Temperature 2: {0:0.2f} C\".format(a.T2))"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {
"nbpages": {
"level": 2,
"link": "[1.2.3 Setting Heaters](https://jckantor.github.io/CBE32338/01.02-The-TCLab-Python-Package.html#1.2.3-Setting-Heaters)",
"section": "1.2.3 Setting Heaters"
}
},
"source": [
"Alternatively, the heaters can be set using the `.U1` and `.U2` attributes of a `TCLab` instance. "
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": 20,
"metadata": {
"nbpages": {
"level": 2,
"link": "[1.2.3 Setting Heaters](https://jckantor.github.io/CBE32338/01.02-The-TCLab-Python-Package.html#1.2.3-Setting-Heaters)",
"section": "1.2.3 Setting Heaters"
}
},
"outputs": [
{
"name": "stdout",
"output_type": "stream",
"text": [
"TCLab version 0.4.8\n",
"Arduino Leonardo connected on port /dev/cu.usbmodem14101 at 115200 baud.\n",
"TCLab Firmware 1.4.3 Arduino Leonardo/Micro.\n",
"Setting power levels on heaters 1 and 2\n",
"Current power level on Heater 1 is: 50.0 %\n",
"Current power level on Heater 1 is: 25.0 %\n",
"TCLab disconnected successfully.\n"
]
}
],
"source": [
"lab = TCLab()\n",
"\n",
"print('Setting power levels on heaters 1 and 2')\n",
"lab.U1 = 50\n",
"lab.U2 = 25\n",
"\n",
"print('Current power level on Heater 1 is: ', lab.U1, '%')\n",
"print('Current power level on Heater 1 is: ', lab.U2, '%')\n",
"\n",
"lab.close()"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {
"nbpages": {
"level": 2,
"link": "[1.2.4 Synchronizing with Real Time using `clock`](https://jckantor.github.io/CBE32338/01.02-The-TCLab-Python-Package.html#1.2.4-Synchronizing-with-Real-Time-using-`clock`)",
"section": "1.2.4 Synchronizing with Real Time using `clock`"
},
"slideshow": {
"slide_type": "skip"
}
},
"source": [
"## 1.2.4 Synchronizing with Real Time using `clock`\n",
"\n",
"The `tclab` module includes `clock` for synchronizing calculations with real time. `clock(tperiod, tstep)` generates a sequence of iterations over a period of `tperiod` seconds evenly by `tstep` seconds. If `tstep` is omitted then the default period is set to 1 second."
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": 24,
"metadata": {
"nbpages": {
"level": 2,
"link": "[1.2.4 Synchronizing with Real Time using `clock`](https://jckantor.github.io/CBE32338/01.02-The-TCLab-Python-Package.html#1.2.4-Synchronizing-with-Real-Time-using-`clock`)",
"section": "1.2.4 Synchronizing with Real Time using `clock`"
}
},
"outputs": [
{
"name": "stdout",
"output_type": "stream",
"text": [
"0 sec.\n",
"2.0 sec.\n",
"4.0 sec.\n",
"6.0 sec.\n"
]
}
],
"source": [
"from tclab import clock\n",
"\n",
"tperiod = 6\n",
"tstep = 2\n",
"for t in clock(tperiod,tstep):\n",
" print(t, \"sec.\")"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {
"nbpages": {
"level": 2,
"link": "[1.2.4 Synchronizing with Real Time using `clock`](https://jckantor.github.io/CBE32338/01.02-The-TCLab-Python-Package.html#1.2.4-Synchronizing-with-Real-Time-using-`clock`)",
"section": "1.2.4 Synchronizing with Real Time using `clock`"
}
},
"source": [
"There are some considerations to keep in mind when using `clock`. Most important, by its nature Python is not a real-time environment. `clock` makes a best effort to stay in sync with evenly spaced ticks of the real time clock. If, for some reason, the loop falls behind the real time clock, then the generator will skip over the event to get back in sync with the real time clock. Thus the total number of iterations may be less than expected. This behavior is demonstrated in the following cell."
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": 27,
"metadata": {
"nbpages": {
"level": 2,
"link": "[1.2.4 Synchronizing with Real Time using `clock`](https://jckantor.github.io/CBE32338/01.02-The-TCLab-Python-Package.html#1.2.4-Synchronizing-with-Real-Time-using-`clock`)",
"section": "1.2.4 Synchronizing with Real Time using `clock`"
}
},
"outputs": [
{
"name": "stdout",
"output_type": "stream",
"text": [
"0 sec.\n",
"2.0 sec.\n",
"4.0 sec.\n",
"8.0 sec.\n",
"10.0 sec.\n",
"12.0 sec.\n"
]
}
],
"source": [
"from tclab import TCLab, clock\n",
"\n",
"import time\n",
"\n",
"tfinal = 12\n",
"tstep = 2\n",
"for t in clock(tfinal, tstep):\n",
" print(t, \"sec.\")\n",
" \n",
" # insert a long time out between 3 and 5 seconds into the event loop\n",
" if (t > 3) and (t < 5):\n",
" time.sleep(2.2)"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {
"nbpages": {
"level": 3,
"link": "[1.2.4.1 Using `clock` with TCLab](https://jckantor.github.io/CBE32338/01.02-The-TCLab-Python-Package.html#1.2.4.1-Using-`clock`-with-TCLab)",
"section": "1.2.4.1 Using `clock` with TCLab"
}
},
"source": [
"### 1.2.4.1 Using `clock` with TCLab"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": 29,
"metadata": {
"nbpages": {
"level": 3,
"link": "[1.2.4.1 Using `clock` with TCLab](https://jckantor.github.io/CBE32338/01.02-The-TCLab-Python-Package.html#1.2.4.1-Using-`clock`-with-TCLab)",
"section": "1.2.4.1 Using `clock` with TCLab"
}
},
"outputs": [
{
"name": "stdout",
"output_type": "stream",
"text": [
"TCLab version 0.4.8\n",
"Arduino Leonardo connected on port /dev/cu.usbmodem14101 at 115200 baud.\n",
"TCLab Firmware 1.4.3 Arduino Leonardo/Micro.\n",
"\n",
"Set Heater 1 to 100.000000 %\n",
"Set Heater 2 to 100.000000 %\n",
" 0.0 sec: T1 = 24.8 C T2 = 22.8 C\n",
" 1.0 sec: T1 = 24.8 C T2 = 24.1 C\n",
" 2.0 sec: T1 = 24.8 C T2 = 23.2 C\n",
" 3.0 sec: T1 = 24.8 C T2 = 22.8 C\n",
" 4.0 sec: T1 = 24.8 C T2 = 23.2 C\n",
" 5.0 sec: T1 = 25.1 C T2 = 24.1 C\n",
" 6.0 sec: T1 = 25.1 C T2 = 24.1 C\n",
" 7.0 sec: T1 = 25.1 C T2 = 23.2 C\n",
" 8.0 sec: T1 = 25.4 C T2 = 23.2 C\n",
" 9.0 sec: T1 = 25.4 C T2 = 23.5 C\n",
" 10.0 sec: T1 = 25.7 C T2 = 24.4 C\n",
" 11.0 sec: T1 = 25.7 C T2 = 23.5 C\n",
" 12.0 sec: T1 = 25.7 C T2 = 23.5 C\n",
" 13.0 sec: T1 = 26.1 C T2 = 23.5 C\n",
" 14.0 sec: T1 = 26.4 C T2 = 23.8 C\n",
" 15.0 sec: T1 = 26.4 C T2 = 24.8 C\n",
" 16.0 sec: T1 = 26.7 C T2 = 23.8 C\n",
" 17.0 sec: T1 = 26.7 C T2 = 24.1 C\n",
" 18.0 sec: T1 = 27.0 C T2 = 24.1 C\n",
" 19.0 sec: T1 = 27.0 C T2 = 25.1 C\n",
" 20.0 sec: T1 = 27.4 C T2 = 25.4 C\n",
"TCLab disconnected successfully.\n"
]
}
],
"source": [
"from tclab import TCLab, clock\n",
"\n",
"tperiod = 20\n",
"\n",
"# connect to the temperature control lab\n",
"with TCLab() as a:\n",
" # turn heaters on\n",
" a.Q1(100)\n",
" a.Q2(100)\n",
" print(\"\\nSet Heater 1 to {0:f} %\".format(a.Q1()))\n",
" print(\"Set Heater 2 to {0:f} %\".format(a.Q2()))\n",
"\n",
" # report temperatures for the next tperiod seconds\n",
" sfmt = \" {0:5.1f} sec: T1 = {1:0.1f} C T2 = {2:0.1f} C\"\n",
" for t in clock(tperiod):\n",
" print(sfmt.format(t, a.T1, a.T2), flush=True)\n",
" "
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {
"nbpages": {
"level": 2,
"link": "[1.2.5 The TCLab `Historian`](https://jckantor.github.io/CBE32338/01.02-The-TCLab-Python-Package.html#1.2.5-The-TCLab-`Historian`)",
"section": "1.2.5 The TCLab `Historian`"
}
},
"source": [
"## 1.2.5 The TCLab `Historian`"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {
"nbpages": {
"level": 2,
"link": "[1.2.5 The TCLab `Historian`](https://jckantor.github.io/CBE32338/01.02-The-TCLab-Python-Package.html#1.2.5-The-TCLab-`Historian`)",
"section": "1.2.5 The TCLab `Historian`"
}
},
"source": [
"The `Historian` class provides means for data logging. Given an instance `lab` of a TCLab object, `lab.sources` is a list of all data sources and methods to access the data.\n",
"\n",
" lab = TCLab()\n",
" h = Historian(lab.sources)\n",
" \n",
"The historian initializes a data log. The data log is updated by issuing a command\n",
"\n",
" h.update(t)\n",
" \n",
"where `t` marks the current time. The following cell logs 10 seconds of data with a chaning power level to heater 1, then saves the data to a file."
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": 7,
"metadata": {
"nbpages": {
"level": 2,
"link": "[1.2.5 The TCLab `Historian`](https://jckantor.github.io/CBE32338/01.02-The-TCLab-Python-Package.html#1.2.5-The-TCLab-`Historian`)",
"section": "1.2.5 The TCLab `Historian`"
}
},
"outputs": [
{
"name": "stdout",
"output_type": "stream",
"text": [
"TCLab version 0.4.9\n",
"Arduino Leonardo connected on port /dev/cu.usbmodem142101 at 115200 baud.\n",
"TCLab Firmware 1.4.3 Arduino Leonardo/Micro.\n",
"TCLab disconnected successfully.\n"
]
}
],
"source": [
"from tclab import TCLab, clock, Historian\n",
"\n",
"with TCLab() as lab:\n",
" h = Historian(lab.sources)\n",
" for t in clock(10):\n",
" lab.Q1(100 if t <= 5 else 0)\n",
" h.update(t)\n",
" \n",
"h.to_csv('data.csv')"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {
"nbpages": {
"level": 2,
"link": "[1.2.5 The TCLab `Historian`](https://jckantor.github.io/CBE32338/01.02-The-TCLab-Python-Package.html#1.2.5-The-TCLab-`Historian`)",
"section": "1.2.5 The TCLab `Historian`"
}
},
"source": [
"Once saved, data can be read and plotted using the [Pandas Data Analysis Library](https://pandas.pydata.org/) as demonstrated in this cell."
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": 59,
"metadata": {
"nbpages": {
"level": 2,
"link": "[1.2.5 The TCLab `Historian`](https://jckantor.github.io/CBE32338/01.02-The-TCLab-Python-Package.html#1.2.5-The-TCLab-`Historian`)",
"section": "1.2.5 The TCLab `Historian`"
}
},
"outputs": [
{
"name": "stdout",
"output_type": "stream",
"text": [
" Time T1 T2 Q1 Q2\n",
"Time \n",
"0.0 0.0 20.26 19.94 100.0 0.0\n",
"1.0 1.0 20.26 19.94 100.0 0.0\n",
"2.0 2.0 20.26 19.94 100.0 0.0\n",
"3.0 3.0 20.26 19.94 100.0 0.0\n",
"4.0 4.0 20.26 19.94 100.0 0.0\n",
"5.0 5.0 20.26 19.94 100.0 0.0\n",
"6.0 6.0 20.26 19.94 0.0 0.0\n",
"7.0 7.0 20.26 19.94 0.0 0.0\n",
"8.0 8.0 20.26 19.94 0.0 0.0\n",
"9.0 9.0 20.26 19.94 0.0 0.0\n",
"10.0 10.0 20.26 19.94 0.0 0.0\n"
]
},
{
"data": {
"text/plain": [
"
\n",
"\n",
"**_Jupyter notebooks and Python scripts:_**\n",
"The highest level consists of the you code you write to implement control algorithms. This can be done in Jupyter/Python notebooks, directly from Python using a development environment such as Spyder or PyCharm. This repository contains several examples, lessons, and student projects.\n",
"\n",
"**_TCLab:_**\n",
"[TCLab](https://github.com/jckantor/TCLab) consists of a Python library entitled `tclab` that provides high-level access to sensors, heaters, a pseudo-realtime clock. The package includes `TCLab()` class that creates an object to access to the device, an iterator `clock` for synchronizing with a real time clock, `Historian()` class to create objects for data logging, and a `Plotter()` class to visualize data in realtime.\n",
"\n",
"**_TCLab-sketch:_**\n",
"The [TCLab-sketch](https://github.com/jckantor/TCLab-sketch) github repository provides firmware to ensure intrisically safe operation of the Arduino board and shield. The sketch is downloaded to the Arduino using the [Arduino IDE](https://www.arduino.cc/en/Main/Software). Loading firmware to the Arduino is a one-time operation. \n",
"\n",
"**_Arduino:_**\n",
"The hardware platform for the Temperature Control Laboratory. The Python tools and libraries have been tested with the Arduino Uno and Arduino Leonardo boards."
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {
"nbpages": {
"level": 2,
"link": "[1.2.1 Connecting to the Temperature Control Laboratory](https://jckantor.github.io/CBE32338/01.02-The-TCLab-Python-Package.html#1.2.1-Connecting-to-the-Temperature-Control-Laboratory)",
"section": "1.2.1 Connecting to the Temperature Control Laboratory"
},
"slideshow": {
"slide_type": "skip"
}
},
"source": [
"## 1.2.1 Connecting to the Temperature Control Laboratory"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {
"nbpages": {
"level": 3,
"link": "[1.2.1.1 Installation](https://jckantor.github.io/CBE32338/01.02-The-TCLab-Python-Package.html#1.2.1.1-Installation)",
"section": "1.2.1.1 Installation"
},
"slideshow": {
"slide_type": "skip"
}
},
"source": [
"### 1.2.1.1 Installation\n",
"\n",
"The TCLab package is installed from a terminal window (MacOS) or command window (PC) with the command\n",
"\n",
" pip install tclab\n",
"\n",
"Alternatively, the installation can be performed from within a Jupyter/Python notebook with the command\n",
"\n",
" !pip install tclab\n",
"\n",
"There are occasional updates to the library. These can be installed by appending a ` --upgrade` to the above commands and demonstrated in the next cell."
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": 1,
"metadata": {
"nbpages": {
"level": 3,
"link": "[1.2.1.1 Installation](https://jckantor.github.io/CBE32338/01.02-The-TCLab-Python-Package.html#1.2.1.1-Installation)",
"section": "1.2.1.1 Installation"
}
},
"outputs": [
{
"name": "stdout",
"output_type": "stream",
"text": [
"Requirement already up-to-date: tclab in /Users/jeff/opt/anaconda3/lib/python3.7/site-packages (0.4.9)\r\n",
"Requirement already satisfied, skipping upgrade: pyserial in /Users/jeff/opt/anaconda3/lib/python3.7/site-packages (from tclab) (3.4)\r\n"
]
}
],
"source": [
"!pip install tclab --upgrade"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {
"nbpages": {
"level": 3,
"link": "[1.2.1.2 Importing](https://jckantor.github.io/CBE32338/01.02-The-TCLab-Python-Package.html#1.2.1.2-Importing)",
"section": "1.2.1.2 Importing"
},
"slideshow": {
"slide_type": "skip"
}
},
"source": [
"### 1.2.1.2 Importing\n",
" \n",
"Once installed, the `tclab` package can be imported into Python and an instance created with the Python statements\n",
"\n",
" from tclab import TCLab\n",
" lab = TCLab()\n",
"\n",
"TCLab() attempts to find a device connected to a serial port and return a connection. An error is generated if no device is found. The connection should be closed when no longer in use.\n",
"\n",
"The following cell demonstrates this process, and uses the tclab `LED()` function to flash the LED on the Temperature Control Lab for a period of 10 seconds at a 100% brightness level. "
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": 4,
"metadata": {
"nbpages": {
"level": 3,
"link": "[1.2.1.2 Importing](https://jckantor.github.io/CBE32338/01.02-The-TCLab-Python-Package.html#1.2.1.2-Importing)",
"section": "1.2.1.2 Importing"
}
},
"outputs": [
{
"name": "stdout",
"output_type": "stream",
"text": [
"TCLab version 0.4.9\n",
"Arduino Leonardo connected on port /dev/cu.usbmodem142101 at 115200 baud.\n",
"TCLab Firmware 1.4.3 Arduino Leonardo/Micro.\n",
"TCLab disconnected successfully.\n"
]
}
],
"source": [
"from tclab import TCLab\n",
"\n",
"lab = TCLab()\n",
"lab.LED(100)\n",
"lab.close()"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {
"nbpages": {
"level": 3,
"link": "[1.2.1.3 Using TCLab with Python's `with` statement](https://jckantor.github.io/CBE32338/01.02-The-TCLab-Python-Package.html#1.2.1.3-Using-TCLab-with-Python's-`with`-statement)",
"section": "1.2.1.3 Using TCLab with Python's `with` statement"
}
},
"source": [
"### 1.2.1.3 Using TCLab with Python's `with` statement\n",
"\n",
"The Python `with` statement provides a convenient means of setting up and closing a connection to the Temperature Control Laboratory. In particular, the with statement establishes a context where a tclab instance is created, assigned to a variable, and automatically closed upon completion. The `with` statement is the preferred way to connect the Temperature Control Laboratory for most uses."
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": 5,
"metadata": {
"nbpages": {
"level": 3,
"link": "[1.2.1.3 Using TCLab with Python's `with` statement](https://jckantor.github.io/CBE32338/01.02-The-TCLab-Python-Package.html#1.2.1.3-Using-TCLab-with-Python's-`with`-statement)",
"section": "1.2.1.3 Using TCLab with Python's `with` statement"
},
"slideshow": {
"slide_type": "skip"
}
},
"outputs": [
{
"name": "stdout",
"output_type": "stream",
"text": [
"TCLab version 0.4.9\n",
"Arduino Leonardo connected on port /dev/cu.usbmodem142101 at 115200 baud.\n",
"TCLab Firmware 1.4.3 Arduino Leonardo/Micro.\n",
"TCLab disconnected successfully.\n"
]
}
],
"source": [
"from tclab import TCLab\n",
"\n",
"with TCLab() as lab:\n",
" lab.LED(100)"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {
"nbpages": {
"level": 2,
"link": "[1.2.2 Reading Temperatures](https://jckantor.github.io/CBE32338/01.02-The-TCLab-Python-Package.html#1.2.2-Reading-Temperatures)",
"section": "1.2.2 Reading Temperatures"
}
},
"source": [
"## 1.2.2 Reading Temperatures\n",
"\n",
"Once a tclab instance is created and connected to a device, the temperature sensors on the temperature control lab can be acccessed with the attributes `.T1` and `.T2`. For example, given an instance `lab`, the temperatures are accessed as\n",
"\n",
" T1 = lab.T1\n",
" T2 = lab.T2\n",
"\n",
"`lab.T1` and `lab.T2` are read-only properties. Any attempt to set them to a value will return a Python error."
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": 6,
"metadata": {
"nbpages": {
"level": 2,
"link": "[1.2.2 Reading Temperatures](https://jckantor.github.io/CBE32338/01.02-The-TCLab-Python-Package.html#1.2.2-Reading-Temperatures)",
"section": "1.2.2 Reading Temperatures"
}
},
"outputs": [
{
"name": "stdout",
"output_type": "stream",
"text": [
"TCLab version 0.4.9\n",
"Arduino Leonardo connected on port /dev/cu.usbmodem142101 at 115200 baud.\n",
"TCLab Firmware 1.4.3 Arduino Leonardo/Micro.\n",
"Temperature 1: 23.48 C\n",
"Temperature 2: 23.81 C\n",
"TCLab disconnected successfully.\n"
]
}
],
"source": [
"from tclab import TCLab\n",
"\n",
"with TCLab() as a:\n",
" print(\"Temperature 1: {0:0.2f} C\".format(a.T1))\n",
" print(\"Temperature 2: {0:0.2f} C\".format(a.T2))"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {
"nbpages": {
"level": 2,
"link": "[1.2.3 Setting Heaters](https://jckantor.github.io/CBE32338/01.02-The-TCLab-Python-Package.html#1.2.3-Setting-Heaters)",
"section": "1.2.3 Setting Heaters"
},
"slideshow": {
"slide_type": "skip"
}
},
"source": [
"## 1.2.3 Setting Heaters\n",
"\n",
"For legacy reasons, there are two ways to set the power levels of the heaters. \n",
"\n",
"The first way is to the functions`.Q1()` and `.Q2()` of a `TCLab` instance. For example, both heaters can be set to 100% power with the functions\n",
"\n",
" lab = TCLab()\n",
" lab.Q1(100)\n",
" lab.Q2(100)\n",
"\n",
"The device firmware limits the heaters to a range of 0 to 100%. The current value of attributes may be accessed via\n",
"\n",
" Q1 = lab.Q1()\n",
" Q2 = lab.Q2()\n",
" \n",
"Important notes:\n",
"1. The led on the temperature control laboratory will turns from dim to bright when either heater is on.\n",
"2. Closing the TCLab instance turns the heaters off.\n",
"3. The power level of the two heaters may be different. Current versions of the firmware limit maximum power of first heater to 4 watts, and maxium power of the second heater to 2 watts.\n",
"4. In addition to the constraints imposed by the firmware, the power supply may not be capable of providing all of the power needed to operate both heaters at 100%\n",
"5. The values retrieved from these functions may be different than the values set due to the power limits enforced by the device firmware."
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": 18,
"metadata": {
"nbpages": {
"level": 2,
"link": "[1.2.3 Setting Heaters](https://jckantor.github.io/CBE32338/01.02-The-TCLab-Python-Package.html#1.2.3-Setting-Heaters)",
"section": "1.2.3 Setting Heaters"
},
"slideshow": {
"slide_type": "skip"
}
},
"outputs": [
{
"name": "stdout",
"output_type": "stream",
"text": [
"TCLab version 0.4.8\n",
"Arduino Leonardo connected on port /dev/cu.usbmodem14101 at 115200 baud.\n",
"TCLab Firmware 1.4.3 Arduino Leonardo/Micro.\n",
"\n",
"Starting Temperature 1: 23.81 C\n",
"Starting Temperature 2: 23.16 C\n",
"\n",
"Set Heater 1: 100.0 %\n",
"Set Heater 2: 100.0 %\n",
"\n",
"Heat for 30 seconds\n",
"\n",
"Turn Heaters Off\n",
"\n",
"Set Heater 1: 0.0 %\n",
"Set Heater 2: 0.0 %\n",
"\n",
"Final Temperature 1: 28.00 C\n",
"Final Temperature 2: 24.77 C\n",
"TCLab disconnected successfully.\n"
]
}
],
"source": [
"from tclab import TCLab\n",
"import time\n",
"\n",
"with TCLab() as a:\n",
" print(\"\\nStarting Temperature 1: {0:0.2f} C\".format(a.T1),flush=True)\n",
" print(\"Starting Temperature 2: {0:0.2f} C\".format(a.T2),flush=True)\n",
"\n",
" a.Q1(100)\n",
" a.Q2(100)\n",
" print(\"\\nSet Heater 1:\", a.Q1(), \"%\",flush=True)\n",
" print(\"Set Heater 2:\", a.Q2(), \"%\",flush=True)\n",
" \n",
" t_heat = 30\n",
" print(\"\\nHeat for\", t_heat, \"seconds\")\n",
" time.sleep(t_heat)\n",
"\n",
" print(\"\\nTurn Heaters Off\")\n",
" a.Q1(0)\n",
" a.Q2(0)\n",
" print(\"\\nSet Heater 1:\", a.Q1(), \"%\",flush=True)\n",
" print(\"Set Heater 2:\", a.Q2(), \"%\",flush=True)\n",
" \n",
" print(\"\\nFinal Temperature 1: {0:0.2f} C\".format(a.T1))\n",
" print(\"Final Temperature 2: {0:0.2f} C\".format(a.T2))"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {
"nbpages": {
"level": 2,
"link": "[1.2.3 Setting Heaters](https://jckantor.github.io/CBE32338/01.02-The-TCLab-Python-Package.html#1.2.3-Setting-Heaters)",
"section": "1.2.3 Setting Heaters"
}
},
"source": [
"Alternatively, the heaters can be set using the `.U1` and `.U2` attributes of a `TCLab` instance. "
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": 20,
"metadata": {
"nbpages": {
"level": 2,
"link": "[1.2.3 Setting Heaters](https://jckantor.github.io/CBE32338/01.02-The-TCLab-Python-Package.html#1.2.3-Setting-Heaters)",
"section": "1.2.3 Setting Heaters"
}
},
"outputs": [
{
"name": "stdout",
"output_type": "stream",
"text": [
"TCLab version 0.4.8\n",
"Arduino Leonardo connected on port /dev/cu.usbmodem14101 at 115200 baud.\n",
"TCLab Firmware 1.4.3 Arduino Leonardo/Micro.\n",
"Setting power levels on heaters 1 and 2\n",
"Current power level on Heater 1 is: 50.0 %\n",
"Current power level on Heater 1 is: 25.0 %\n",
"TCLab disconnected successfully.\n"
]
}
],
"source": [
"lab = TCLab()\n",
"\n",
"print('Setting power levels on heaters 1 and 2')\n",
"lab.U1 = 50\n",
"lab.U2 = 25\n",
"\n",
"print('Current power level on Heater 1 is: ', lab.U1, '%')\n",
"print('Current power level on Heater 1 is: ', lab.U2, '%')\n",
"\n",
"lab.close()"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {
"nbpages": {
"level": 2,
"link": "[1.2.4 Synchronizing with Real Time using `clock`](https://jckantor.github.io/CBE32338/01.02-The-TCLab-Python-Package.html#1.2.4-Synchronizing-with-Real-Time-using-`clock`)",
"section": "1.2.4 Synchronizing with Real Time using `clock`"
},
"slideshow": {
"slide_type": "skip"
}
},
"source": [
"## 1.2.4 Synchronizing with Real Time using `clock`\n",
"\n",
"The `tclab` module includes `clock` for synchronizing calculations with real time. `clock(tperiod, tstep)` generates a sequence of iterations over a period of `tperiod` seconds evenly by `tstep` seconds. If `tstep` is omitted then the default period is set to 1 second."
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": 24,
"metadata": {
"nbpages": {
"level": 2,
"link": "[1.2.4 Synchronizing with Real Time using `clock`](https://jckantor.github.io/CBE32338/01.02-The-TCLab-Python-Package.html#1.2.4-Synchronizing-with-Real-Time-using-`clock`)",
"section": "1.2.4 Synchronizing with Real Time using `clock`"
}
},
"outputs": [
{
"name": "stdout",
"output_type": "stream",
"text": [
"0 sec.\n",
"2.0 sec.\n",
"4.0 sec.\n",
"6.0 sec.\n"
]
}
],
"source": [
"from tclab import clock\n",
"\n",
"tperiod = 6\n",
"tstep = 2\n",
"for t in clock(tperiod,tstep):\n",
" print(t, \"sec.\")"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {
"nbpages": {
"level": 2,
"link": "[1.2.4 Synchronizing with Real Time using `clock`](https://jckantor.github.io/CBE32338/01.02-The-TCLab-Python-Package.html#1.2.4-Synchronizing-with-Real-Time-using-`clock`)",
"section": "1.2.4 Synchronizing with Real Time using `clock`"
}
},
"source": [
"There are some considerations to keep in mind when using `clock`. Most important, by its nature Python is not a real-time environment. `clock` makes a best effort to stay in sync with evenly spaced ticks of the real time clock. If, for some reason, the loop falls behind the real time clock, then the generator will skip over the event to get back in sync with the real time clock. Thus the total number of iterations may be less than expected. This behavior is demonstrated in the following cell."
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": 27,
"metadata": {
"nbpages": {
"level": 2,
"link": "[1.2.4 Synchronizing with Real Time using `clock`](https://jckantor.github.io/CBE32338/01.02-The-TCLab-Python-Package.html#1.2.4-Synchronizing-with-Real-Time-using-`clock`)",
"section": "1.2.4 Synchronizing with Real Time using `clock`"
}
},
"outputs": [
{
"name": "stdout",
"output_type": "stream",
"text": [
"0 sec.\n",
"2.0 sec.\n",
"4.0 sec.\n",
"8.0 sec.\n",
"10.0 sec.\n",
"12.0 sec.\n"
]
}
],
"source": [
"from tclab import TCLab, clock\n",
"\n",
"import time\n",
"\n",
"tfinal = 12\n",
"tstep = 2\n",
"for t in clock(tfinal, tstep):\n",
" print(t, \"sec.\")\n",
" \n",
" # insert a long time out between 3 and 5 seconds into the event loop\n",
" if (t > 3) and (t < 5):\n",
" time.sleep(2.2)"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {
"nbpages": {
"level": 3,
"link": "[1.2.4.1 Using `clock` with TCLab](https://jckantor.github.io/CBE32338/01.02-The-TCLab-Python-Package.html#1.2.4.1-Using-`clock`-with-TCLab)",
"section": "1.2.4.1 Using `clock` with TCLab"
}
},
"source": [
"### 1.2.4.1 Using `clock` with TCLab"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": 29,
"metadata": {
"nbpages": {
"level": 3,
"link": "[1.2.4.1 Using `clock` with TCLab](https://jckantor.github.io/CBE32338/01.02-The-TCLab-Python-Package.html#1.2.4.1-Using-`clock`-with-TCLab)",
"section": "1.2.4.1 Using `clock` with TCLab"
}
},
"outputs": [
{
"name": "stdout",
"output_type": "stream",
"text": [
"TCLab version 0.4.8\n",
"Arduino Leonardo connected on port /dev/cu.usbmodem14101 at 115200 baud.\n",
"TCLab Firmware 1.4.3 Arduino Leonardo/Micro.\n",
"\n",
"Set Heater 1 to 100.000000 %\n",
"Set Heater 2 to 100.000000 %\n",
" 0.0 sec: T1 = 24.8 C T2 = 22.8 C\n",
" 1.0 sec: T1 = 24.8 C T2 = 24.1 C\n",
" 2.0 sec: T1 = 24.8 C T2 = 23.2 C\n",
" 3.0 sec: T1 = 24.8 C T2 = 22.8 C\n",
" 4.0 sec: T1 = 24.8 C T2 = 23.2 C\n",
" 5.0 sec: T1 = 25.1 C T2 = 24.1 C\n",
" 6.0 sec: T1 = 25.1 C T2 = 24.1 C\n",
" 7.0 sec: T1 = 25.1 C T2 = 23.2 C\n",
" 8.0 sec: T1 = 25.4 C T2 = 23.2 C\n",
" 9.0 sec: T1 = 25.4 C T2 = 23.5 C\n",
" 10.0 sec: T1 = 25.7 C T2 = 24.4 C\n",
" 11.0 sec: T1 = 25.7 C T2 = 23.5 C\n",
" 12.0 sec: T1 = 25.7 C T2 = 23.5 C\n",
" 13.0 sec: T1 = 26.1 C T2 = 23.5 C\n",
" 14.0 sec: T1 = 26.4 C T2 = 23.8 C\n",
" 15.0 sec: T1 = 26.4 C T2 = 24.8 C\n",
" 16.0 sec: T1 = 26.7 C T2 = 23.8 C\n",
" 17.0 sec: T1 = 26.7 C T2 = 24.1 C\n",
" 18.0 sec: T1 = 27.0 C T2 = 24.1 C\n",
" 19.0 sec: T1 = 27.0 C T2 = 25.1 C\n",
" 20.0 sec: T1 = 27.4 C T2 = 25.4 C\n",
"TCLab disconnected successfully.\n"
]
}
],
"source": [
"from tclab import TCLab, clock\n",
"\n",
"tperiod = 20\n",
"\n",
"# connect to the temperature control lab\n",
"with TCLab() as a:\n",
" # turn heaters on\n",
" a.Q1(100)\n",
" a.Q2(100)\n",
" print(\"\\nSet Heater 1 to {0:f} %\".format(a.Q1()))\n",
" print(\"Set Heater 2 to {0:f} %\".format(a.Q2()))\n",
"\n",
" # report temperatures for the next tperiod seconds\n",
" sfmt = \" {0:5.1f} sec: T1 = {1:0.1f} C T2 = {2:0.1f} C\"\n",
" for t in clock(tperiod):\n",
" print(sfmt.format(t, a.T1, a.T2), flush=True)\n",
" "
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {
"nbpages": {
"level": 2,
"link": "[1.2.5 The TCLab `Historian`](https://jckantor.github.io/CBE32338/01.02-The-TCLab-Python-Package.html#1.2.5-The-TCLab-`Historian`)",
"section": "1.2.5 The TCLab `Historian`"
}
},
"source": [
"## 1.2.5 The TCLab `Historian`"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {
"nbpages": {
"level": 2,
"link": "[1.2.5 The TCLab `Historian`](https://jckantor.github.io/CBE32338/01.02-The-TCLab-Python-Package.html#1.2.5-The-TCLab-`Historian`)",
"section": "1.2.5 The TCLab `Historian`"
}
},
"source": [
"The `Historian` class provides means for data logging. Given an instance `lab` of a TCLab object, `lab.sources` is a list of all data sources and methods to access the data.\n",
"\n",
" lab = TCLab()\n",
" h = Historian(lab.sources)\n",
" \n",
"The historian initializes a data log. The data log is updated by issuing a command\n",
"\n",
" h.update(t)\n",
" \n",
"where `t` marks the current time. The following cell logs 10 seconds of data with a chaning power level to heater 1, then saves the data to a file."
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": 7,
"metadata": {
"nbpages": {
"level": 2,
"link": "[1.2.5 The TCLab `Historian`](https://jckantor.github.io/CBE32338/01.02-The-TCLab-Python-Package.html#1.2.5-The-TCLab-`Historian`)",
"section": "1.2.5 The TCLab `Historian`"
}
},
"outputs": [
{
"name": "stdout",
"output_type": "stream",
"text": [
"TCLab version 0.4.9\n",
"Arduino Leonardo connected on port /dev/cu.usbmodem142101 at 115200 baud.\n",
"TCLab Firmware 1.4.3 Arduino Leonardo/Micro.\n",
"TCLab disconnected successfully.\n"
]
}
],
"source": [
"from tclab import TCLab, clock, Historian\n",
"\n",
"with TCLab() as lab:\n",
" h = Historian(lab.sources)\n",
" for t in clock(10):\n",
" lab.Q1(100 if t <= 5 else 0)\n",
" h.update(t)\n",
" \n",
"h.to_csv('data.csv')"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {
"nbpages": {
"level": 2,
"link": "[1.2.5 The TCLab `Historian`](https://jckantor.github.io/CBE32338/01.02-The-TCLab-Python-Package.html#1.2.5-The-TCLab-`Historian`)",
"section": "1.2.5 The TCLab `Historian`"
}
},
"source": [
"Once saved, data can be read and plotted using the [Pandas Data Analysis Library](https://pandas.pydata.org/) as demonstrated in this cell."
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": 59,
"metadata": {
"nbpages": {
"level": 2,
"link": "[1.2.5 The TCLab `Historian`](https://jckantor.github.io/CBE32338/01.02-The-TCLab-Python-Package.html#1.2.5-The-TCLab-`Historian`)",
"section": "1.2.5 The TCLab `Historian`"
}
},
"outputs": [
{
"name": "stdout",
"output_type": "stream",
"text": [
" Time T1 T2 Q1 Q2\n",
"Time \n",
"0.0 0.0 20.26 19.94 100.0 0.0\n",
"1.0 1.0 20.26 19.94 100.0 0.0\n",
"2.0 2.0 20.26 19.94 100.0 0.0\n",
"3.0 3.0 20.26 19.94 100.0 0.0\n",
"4.0 4.0 20.26 19.94 100.0 0.0\n",
"5.0 5.0 20.26 19.94 100.0 0.0\n",
"6.0 6.0 20.26 19.94 0.0 0.0\n",
"7.0 7.0 20.26 19.94 0.0 0.0\n",
"8.0 8.0 20.26 19.94 0.0 0.0\n",
"9.0 9.0 20.26 19.94 0.0 0.0\n",
"10.0 10.0 20.26 19.94 0.0 0.0\n"
]
},
{
"data": {
"text/plain": [
"