This notebook contains material from cbe30338-2021; content is available on Github.
The purpose of this notebook is to describe a technological challenge requiring the use of the feedback control for a satisfactory result. Here we consider performance requirements for a thermal cycling device used for diagnostic testing based on the polymerase chain reaction (PCR). These devices are used to exponentially "amplify" segments of DNA that may be present in biological samples. These devices are ubiquitous in modern biology laboraties and medical testing services.
In this notebook we will review:
The learning goals are for student to able to:
COVID-19 is a respiratory tract infection by a specific species of coronavirus called SARS-CoV-2. Coronaviruses have a protein envelope characterized by club-shaped protrusions that give the impression of a corona when viewed with an electron microscope.
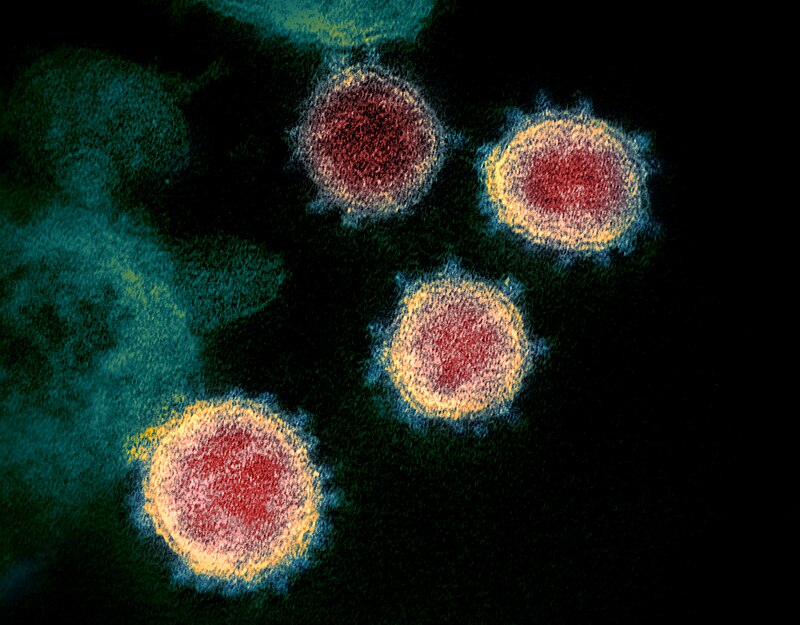
By NIAID - https://www.flickr.com/photos/niaid/49534865371/, CC BY 2.0, Link
Coronaviruses have a relatively large genome comprised of a single strand of positive-sense RNA.
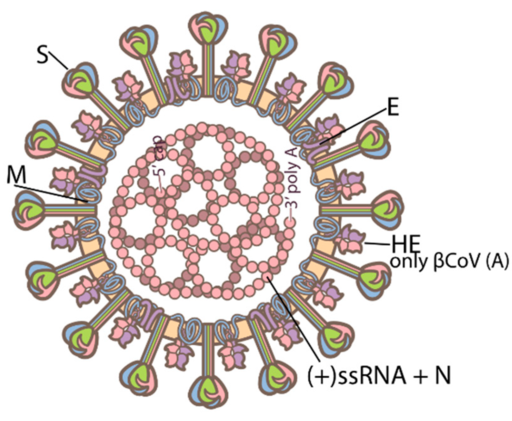
https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Vaccines-08-00587-g002-A.png
A coronavirus test begins with a swab of throat or nose. The swab is rinsed with a buffer solution to capture the host DNA and RNA, and the RNA of any virus that may be present. RNA is isolated from the solution and converted to DNA using a reverse transcriptase enzyme. The amount of DNA collected in this fashion is too small to analyze by conventional methods. So the first step in a diagnostic protocol is to amplify the amount of DNA using the polymerase chain reaction.
The polymerase chain reaction (PCR) is a technique used in molecular biology to take amplify small samples of DNA into quantities large enough to be detected using conventional analytical methods. The technique is described in the following videos.
from IPython.lib.display import YouTubeVideo
YouTubeVideo('2KoLnIwoZKU')
from IPython.lib.display import YouTubeVideo
YouTubeVideo('c07_5BfIDTw')
PCR provides an exponential amplification of target DNA sequences to concentrations that can be detected by conventional analytical techniques.

https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Polymerase_chain_reaction-en.svg
The main part of PCR consists of three steps that are repeated 20 or more times:
PCR thermal cyclers are a common piece of hardware in biology and medical testing laboratories. These devices automate the thermal cycle operation by providing users with convenient means of specifying parameters for a particular PCR test, and then executing that cycle to some specified degree of precision. Most commercial devices perform multiple from a few to several hundres tests at a time.

There are also examples of low-cost and open-source designs of PCR thermal cyclers intended for education, field work, and other situations where there is a benefit to keeping costs very low.
from IPython.display import YouTubeVideo
YouTubeVideo('ALNZJhUOSMs')
With two heater/sensor assemblies, the temperature Control Lab provides a platform for developing and testing control strategies for a PCR thermal cycler.

There are some differences. PCR thermal cyclers generally include thermoelectric coolers rather than rely solely on convective cooling, and generally have more "control authority" in the form of larger power inputs. So we will be limited in our ability to mimic higher performance devices. But for the purposes of prototyping, the Temperature Contol Lab offers an excellent platform for initial prototype.
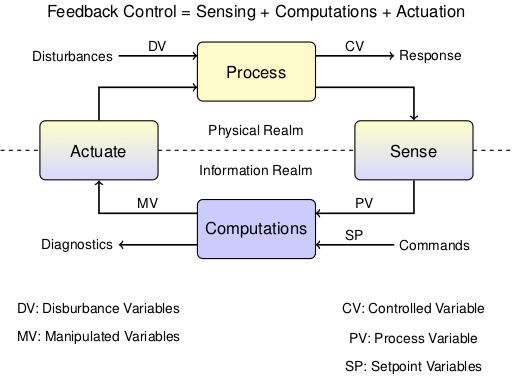
Consider the use of the Temperature Control Lab as a prototyping device for a PCR Thermal Cycling device. Discuss each of the following aspects of the control loop:
In qualitative terms, describe: