6.2. Maximizing Concentration of an Intermediate in a Batch Reactor#
Keywords: ipopt usage, scipy.minimize_scalar, scipy.odeint, unconstrained optimization
This notebook presents an example of the finding the time period required to achieve an optimal result. Because the period of operation is an unknown
6.2.1. Problem Statement#
A desired product \(B\) is as an intermediate in a series reactions
where \(A\) is a raw material and \(C\) is an undesired by-product. The reaction operates isothermally with rate constants \(k_A = 0.5\ \mbox{min}^{-1}\) and \(k_B = 0.1\ \mbox{min}^{-1}\). The raw material is a solution with concentration \(C_{A,f} = 2.0\ \mbox{moles/liter}\).
A 100 liter tank is available for use as a batch reactor. How long should the reaction be operated to maximize the concentration of \(B\)?
6.2.2. Imports#
%matplotlib inline
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
from scipy.integrate import odeint
from scipy.optimize import minimize_scalar
import shutil
import sys
import os.path
if not shutil.which("pyomo"):
!pip install -q pyomo
assert(shutil.which("pyomo"))
if not (shutil.which("ipopt") or os.path.isfile("ipopt")):
if "google.colab" in sys.modules:
!wget -N -q "https://ampl.com/dl/open/ipopt/ipopt-linux64.zip"
!unzip -o -q ipopt-linux64
else:
try:
!conda install -c conda-forge ipopt
except:
pass
assert(shutil.which("ipopt") or os.path.isfile("ipopt"))
from pyomo.environ import *
from pyomo.dae import *
6.2.3. Mathematical model#
A material balance for an isothermal stirred batch reactor with a volume \(V = 40\) liters and an initial concentration \(C_{A,f}\) is given by
Eliminating the common factor \(V\)
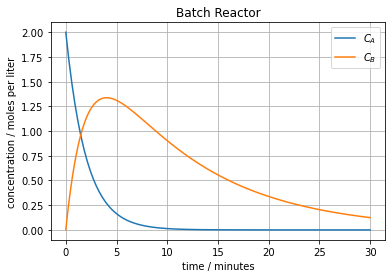
With an initial concentration \(C_{A,f}\). A numerical solution to these equations is shown in the following cell.
V = 40 # liters
kA = 0.5 # 1/min
kB = 0.1 # l/min
CAf = 2.0 # moles/liter
def batch(X, t):
CA, CB = X
dCA_dt = -kA*CA
dCB_dt = kA*CA - kB*CB
return [dCA_dt, dCB_dt]
t = np.linspace(0,30,200)
soln = odeint(batch, [CAf,0], t)
plt.plot(t, soln)
plt.xlabel('time / minutes')
plt.ylabel('concentration / moles per liter')
plt.title('Batch Reactor')
plt.legend(['$C_A$','$C_B$'])
plt.grid(True)
6.2.4. Optimization with scipy.minimize_scalar#
To find the maximum value, we first write a function to compute \(C_B\) for any value of time \(t\).
def CB(tf):
soln = odeint(batch, [CAf, 0], [0, tf])
return soln[-1][1]
We gain use minimize_scalar to find the value of \(t\) that minimizes the negative value of \(C_B(t)\).|
minimize_scalar(lambda t: -CB(t), bracket=[0, 50])
fun: -1.3374806339222158
message: '\nOptimization terminated successfully;\nThe returned value satisfies the termination criteria\n(using xtol = 1.48e-08 )'
nfev: 23
nit: 19
success: True
x: 4.023594924340666
tmax = minimize_scalar(lambda t: -CB(t), bracket=[0,50]).x
print('Concentration c_B has maximum', CB(tmax), 'moles/liter at time', tmax, 'minutes.')
Concentration c_B has maximum 1.3374806339222158 moles/liter at time 4.023594924340666 minutes.
6.2.5. Solution using Pyomo#
The variable to be found is the time \(t_f\) corresponding to the maximum concentration of \(B\). For this purpose we introduce a scaled time
so that \(\tau=1\) as the desired solution. The problem then reads
subject to
The solution to this problem is implemented as a solution to the following Pyomo model.
V = 40 # liters
kA = 0.5 # 1/min
kB = 0.1 # l/min
cAf = 2.0 # moles/liter
m = ConcreteModel()
m.tau = ContinuousSet(bounds=(0, 1))
m.tf = Var(domain=NonNegativeReals)
m.cA = Var(m.tau, domain=NonNegativeReals)
m.cB = Var(m.tau, domain=NonNegativeReals)
m.dcA = DerivativeVar(m.cA)
m.dcB = DerivativeVar(m.cB)
m.odeA = Constraint(m.tau,
rule=lambda m, tau: m.dcA[tau] == m.tf*(-kA*m.cA[tau]) if tau > 0 else Constraint.Skip)
m.odeB = Constraint(m.tau,
rule=lambda m, tau: m.dcB[tau] == m.tf*(kA*m.cA[tau] - kB*m.cB[tau]) if tau > 0 else Constraint.Skip)
m.ic = ConstraintList()
m.ic.add(m.cA[0] == cAf)
m.ic.add(m.cB[0] == 0)
m.obj = Objective(expr=m.cB[1], sense=maximize)
TransformationFactory('dae.collocation').apply_to(m)
SolverFactory('ipopt').solve(m)
print('Concentration c_B has maximum', m.cB[1](), 'moles/liter at time', m.tf(), 'minutes.')
Concentration c_B has maximum 1.3374805810221082 moles/liter at time 4.023594178375689 minutes.